Orthognathic Surgery
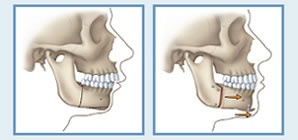 Orthognathic surgery is the surgical correction of skeletal deformities of the oral and maxillofacial region and is necessary for patients with an improper bite or whose jaws are positioned incorrectly. Since jaw growth is a gradual process, sometimes the upper and lower jaws may grow at different rates, leading to problems that can affect speech, appearance, chewing, and long-term oral health. A birth defect, an injury, and environmental influences or heredity can also affect jaw alignment. Signs of possibly being a candidate for orthognathic surgery, that should be discussed with your doctor include: protruding jaw, speech problems, an open bite, chronic jaw pain, and difficulty in chewing or biting.
Orthognathic surgery is the surgical correction of skeletal deformities of the oral and maxillofacial region and is necessary for patients with an improper bite or whose jaws are positioned incorrectly. Since jaw growth is a gradual process, sometimes the upper and lower jaws may grow at different rates, leading to problems that can affect speech, appearance, chewing, and long-term oral health. A birth defect, an injury, and environmental influences or heredity can also affect jaw alignment. Signs of possibly being a candidate for orthognathic surgery, that should be discussed with your doctor include: protruding jaw, speech problems, an open bite, chronic jaw pain, and difficulty in chewing or biting.
Making a decision to proceed with treatment will also involve the participation of an orthodontist, who will work closely with your doctor during your treatment. Orthodontics alone is designed for patients whose teeth need to be straightened and/or whose bite problems can be solved with just moving the teeth. Orthognathic surgery however, is specially tailored for those patients where there is bone/skeletal incongruity. By re-positioning the jaws in coordination with orthodontic alignment of the teeth, the facial appearance can be enhanced or improved. The result of having this corrective jaw surgery is not only enhanced facial appearance and functioning, but it also ensures the teeth meet correctly and function properly, leading to a new healthy dental-facial relationship.
